Psychosocial:
- “Of or relating to processes or factors that are both social and psychological in origin”
Search: Psychosocial. Retrieved from Dictioanary.com at : http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/psychosocial
- “Refers to the close connection between psychological aspects of human experience and the wider social experience. “
Search: Psychosocial. Retrieved from ARC resource pack at: http://www.refworld.org/pdfid/4b55dabe2.pdf
Types of Psychosocial issues
- Depression and Anxiety
- Grief and Bereavement
- Financial Issues, Insurance and Benefits
- Substance Abuse
- Social Isolation and Loneliness
- Loss of Independence
- Housing Status Changed
- Crime and Abuse/Neglect\
List derived from : http://www.cornellcares.org/education/pdf/Psychosocial_Orientaton_10-11.pdf
Psychosocial Support :
3.“Is a scale of care and support which influences both the individual and the social environment in which people live and ranges from care and support offered by caregivers, family members, friends, neighbors, teachers, health workers, and community members on a daily basis but also extends to care and support offered by specialized psychological and social services. “
Search: Psychological Support. Retrieved from ARC resource pack at: http://www.refworld.org/pdfid/4b55dabe2.pdf
Mental Health :
4. “Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which every individual realizes his or her own potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to her or his community.”
Search: Mental Health. Retrieved from the World Health Organization at : http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/mental_health/en/
- World Health Organization
Several organizations have made it an effort to provide many refugee/ asylum seekers with programs to treat any mental trauma that a person may develop due to traumatic circumstances. WHO is an example of an organization who’s main focus is to provide refugee/ asylum seeking peoples with treatment and support for any trauma they may incur during the application process.
World Health Organization : http://www.who.int/mental_health/emergencies/en/
- UNHCR- The UN Refugee Agency
UNHCR acknowledges the impact that displacement, war, sickness and having to deal with loss can put on individuals as well as their family. This being said, they ensure that they are providing opportunities for refugee and asylum seekers to better their mental health, and cope with social stresses. The UNHCR’s guidance report for Mental health and Psychological support outlines in detail how humanitarian actors should be treating these people.
United Nations High Commissioners for Refugees: http://www.unhcr.org/525f94479.pdf
- IASC Mental Health and Psychosocial Support
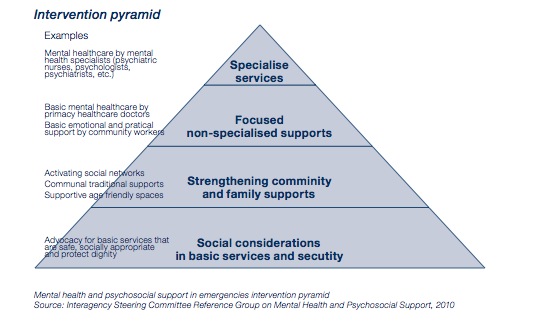
There are different levels of mental health and psychosocial help that can be received depending on the level of trauma a person has undergone. Ranging from simply needing the basic necessities of food, shelter and water, to getting psychiatric help to deal with trauma that disrupts daily functions, and IASC is determined to ensure that there is the right amount of care available at any stage. The above diagram provides examples for each level of care.
IASC Guidelines on Mental Health and Psychosocial Support in Emergency Settings. Geneva: IASC, Inter-Agency Standing Committee, 2007. PDF. < http://www.who.int/mental_health/emergencies/guidelines_iasc_mental_health_psychosocial_june_2007.pdf>
- United Nations- Department of Economic and Social Affairs
The UN’s department of Economic and Social Affairs focuses largely on Youth with mental health issues, and helping them integrate into society. This effort does not only limit itself to those seeking asylum or refuge, however focuses on the mental health of youth who have been abused, bullied, live in poverty, and the programs that have been made available to these children and their families, provide a chance for self development.
-“Mental Health Matters: Social Inclusion of Youth with Mental Health Conditions.” Refworld. United Nations, 2014. Web. 27 Oct. 2014. http://www.refworld.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/rwmain?page=search&docid=53f1be4c4&skip=0&query=mental%20health
Andemicael, Awet. “Positive Energy: A Review of the Role of Artistic Activities in Refugee Camps.” Refworld. UN High Commissioner for Refugees, June 2011. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.refworld.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/rwmain?page=search&docid=4e4b73ad2&skip=0&query=psychosocial,%20refugees>.
Karachiwalla, Fareen I. “Mental Health Considerations in Refugee Populations.” (n.d.): n. pag. UBCMJ. Mar. 2011. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.ubcmj.com/pdf/ubcmj_2_2_2011_20-22.pdf>.
“Mental Health and Psychosocial Support in Humanitarian Emergencies – What Should Protection Program Managers Know?” Refworld. Inter-Agency Standing Committee, Jan. 2010. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.refworld.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/rwmain?page=search&docid=4e97d2d12&skip=0&query=psychosocial>.
Meyer, Sarah. “UNHCR’s Mental Health and Psychosocial Support for Persons of Concern.” Refworld. UN High Commissioner for Refugees, June 2013. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.refworld.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/rwmain?page=search&docid=51de9f7a4&skip=0&query=psychosocial>.
“Psychosocial Support for Refugees and Asylum Seekers in South Africa.” UNHCR. N.p., n.d. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.unhcr.org/4b4dcfea9.html>.
“Psychosocial Support.” ARC Resource Pack. N.p., n.d. Web. 26 Oct. 2014. <http://www.arc-online.org/foundation/psychosocialsupport.html>.
- Trauma
- Psychology
- Stress
- Integration
- Migration
- Emotional